Unleash the Power of Your Digital Elevation Model

Unleash the Power of Your Digital Elevation Model
As the volume of elevation data continues to grow, thanks to both public repositories and drone captures, the question arises: How can one effectively process and visualise Digital Elevation Models (DEMs)? And, once you have generated a DEM how can you maximize its usage. Dive into this blog post for invaluable insights
Using the tools available in the ArcGIS system, you can process and visualise your DEM and create numerous data products that will help you further your analysis.
How do I convert my raster tiles into one raster file?
If the data you have downloaded is stored in a series of raster you will need to process these raster tiles into a usable format for analysis. You can achieve this with a few simple steps.
- create a raster dataset,
- add the raster tiles to the raster dataset,
- and run the Mosaic To New Raster data management tool. This tool will process the tiles into one raster file in a simple step.
Check out how the tool works here or watch this quick video - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ctIIf1xlMZU
How can I improve a noisy DEM?
The capture of high-resolution data, such as LiDAR, may result in a "noisy" DEM characterised by the inclusion of excessive surface details (noise). If your LiDAR data includes a model-key class this can be used to reduce the noise. If your LiDAR data does not include a model-key class you will need to apply a workflow that involves thinning of the raw data, creation of a terrain dataset, and rasterization of a terrain dataset. How to create a terrain dataset with thinning applied is documented here.
Another approach to removing noise is to use the spatial analyst extension generalisation tools such as Nibble or Majority filter.
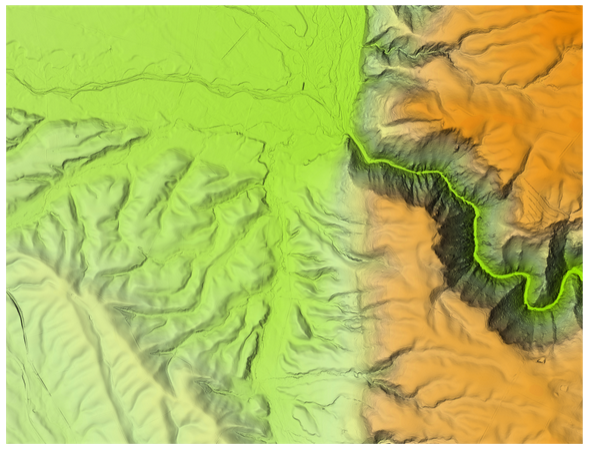
How do I flatten rivers in a DEM?
LiDAR-captured data introduces water bodies, such as rivers or lakes, that are not perfectly flat. Using tools in ArcGIS Pro version 3.0 or higher, in conjunction with the 3D Analyst extension, you can rectify this issue. The Enforce River Monotonicity tool ensures that Z values for water features follow a unidirectional pattern. Pre-processing of data is required before applying this tool.
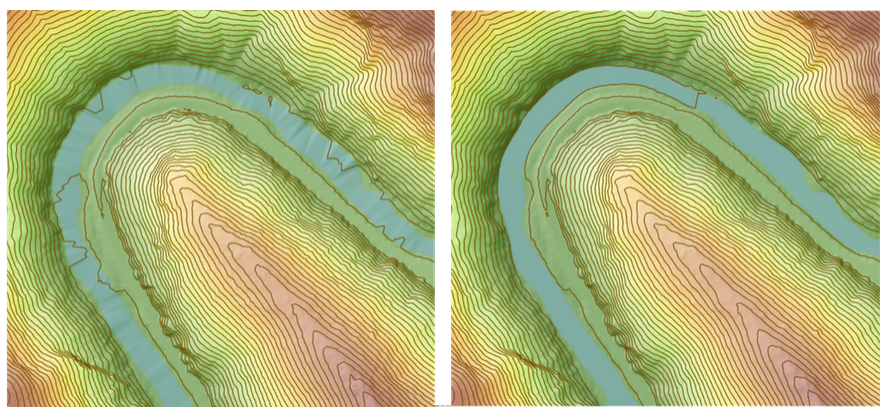
The full workflow is outlined here.
How can I make a relative elevation model?
When you aim to generate maps illustrating elevation in relation to a river surface, employing the relative elevation model technique is effective. Relative elevation models are a fantastic way to show fluvial landforms like river meandering, erosion, and floodplains more clearly. Check out this Esri video at https://mediaspace.esri.com/media/t/1_pn5ltf54 if you would like more details of this process.
What products can I create from DEM?
A DEM is a versatile dataset and it can be used 'as is' but the value of it does not stop there. You can create several products from a DEM. The most common products are:
- Hillshade
- A Slope raster
- An Aspect raster
- Contours
These products can be created using a single geoprocessing tool or raster function.
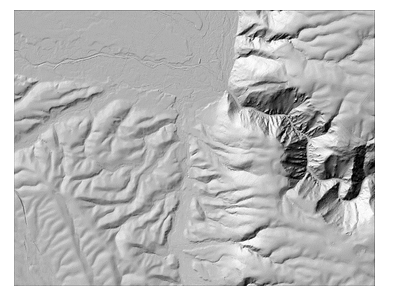
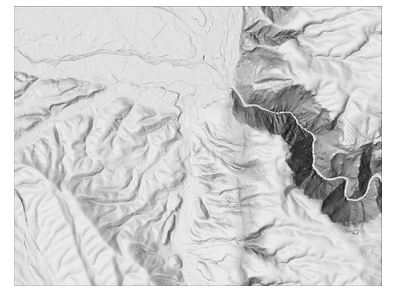
Hillshade
This is a classic representation of a terrain using simulated sunlight from northwest.
Opting to create a hillshade using the ArcGIS Pro Hillshade raster function, as opposed to the Hillshade geoprocessing tool, provides the advantage of employing the more advanced technique of multidirectional hillshade. This enhances the visualisation of terrain morphology.
 |
 |
|
| Standard hillshade | Multidirectional hillshade |
Slope
Slope is the tool most used to create derivate DEM products. To create slope rasters we recommend the Surface Parameters tool instead of the Slope tool. The surface parameter tool calculates slope using newer and more enhanced functionalities than the slope tool. This tool also can produce aspect and different curvature rasters.
Aspect
Aspect maps depict the direction of the slope face. To create an aspect map geoprocessing tool and a raster function are available. If you prefer to use raster functions, there is an option to combine aspect and slope in a single output using a single Aspect-Slope raster function.
| Aspect | Aspect Slope |
Contours
As with other products, geoprocessing tool and raster functions are available to create contour lines showing lines of the same elevation.
Shaded relief
For cartographic purposes, you can create a shaded relief in a single step using the Shaded Relief raster function. To produce the relief, you can choose a traditional hillshade or a multidirectional one. You can use the standard colour ramp to display your shaded relief or download additional ones from ArcGIS Online or even create your own.
How can I render a DEM in a map?
Using the default colour ramp to render a DEM can make visualisation difficult. Therefore, there are numerous techniques to improve visualisation, the most common is to generate a hillshade from a DEM. Once you have a hillshade, there are plenty of options to enhance your visualisation by using the Layer Blend options. A simple cartography hack is to place your hillshade layer just above the imagery basemap and set Layer Blend to Multiply mode.
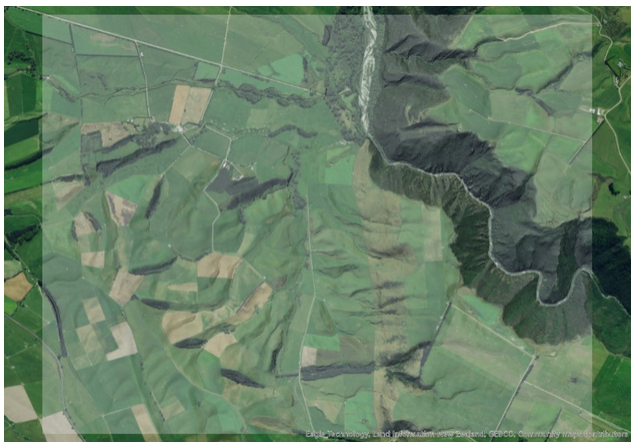

Transparency on hillshade
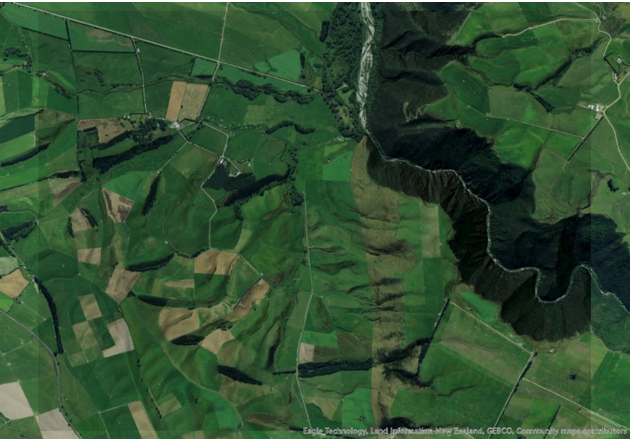

Layer blending of a hillshade and a basemap
For more DEM visualisation tips and tricks visit John Nelson on Esri's blog and his YouTube channel.
In conclusion, the Unleashing the power of your Digital Elevation Model (DEM) blog opens up a world of possibilities for advanced geospatial analysis. We have provided key insights into processing and visualising DEMs effectively, including techniques from merging raster tiles to refining noisy DEMs to flattening rivers. Don't forget to click the links that provide additional references throughout this blog.
